Dna Replikation Ligase Funktion | The gaps between okazaki fragments and new dna fragments are joined by ligase. Jump to navigationjump to search. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. Coli, dna replication begins by the binding of dnaa proteins to 5 sequences within the origin known as dnaa box sequences (hu an ihf also bind).
After ligation, the insert dna is physically attached to the backbone and the complete plasmid can be transformed into bacterial cells for propagation. This completes the synthesis of the lagging strand. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Dna replication is the process in which new copy of dna is produced from parent dna. The gaps between okazaki fragments and new dna fragments are joined by ligase.

Coli, dna replication begins by the binding of dnaa proteins to 5 sequences within the origin known as dnaa box sequences (hu an ihf also bind). Anyone should feel free to add themselves as a curator for this consensus protocol. Okazaki fragments are formed on the lagging strand, while the leading strand is replicated continuously. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. 2.7 dna replication, transcription, translation. When two strand of dna are separated, each strand act as dna ligase joins these okazaki fragments to form complete lagging strands. Dna polymerase i is brought in to remove and replace. James hadfield, cruk cambridge research institute, robinson way, cambridge cb2 0re. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. There are give different dna replication that started at one origin of replication has met that progressing from the other mistakes are identified. Restriction enzymes & dna ligase. Since the direction of movement of replication fork is opposite to direction. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound.
This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. Dna ligase to join up. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or old strand. This completes the synthesis of the lagging strand. Dna polymerase i is brought in to remove and replace.
Since the direction of movement of replication fork is opposite to direction. Joins okazaki fragments during dna replication. Dna replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna. Dna polymerase i is brought in to remove and replace. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. Dna replication is the process in which new copy of dna is produced from parent dna. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. Coli, dna replication begins by the binding of dnaa proteins to 5 sequences within the origin known as dnaa box sequences (hu an ihf also bind). Dna ligase i most homologous to sccdc9. Dna replication is a process in which new dna is formed (copying dna). When two strand of dna are separated, each strand act as dna ligase joins these okazaki fragments to form complete lagging strands. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments.
Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. Anyone should feel free to add themselves as a curator for this consensus protocol. • contains other dna ligases (9) but cdc9 is involved in dna replication. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand.
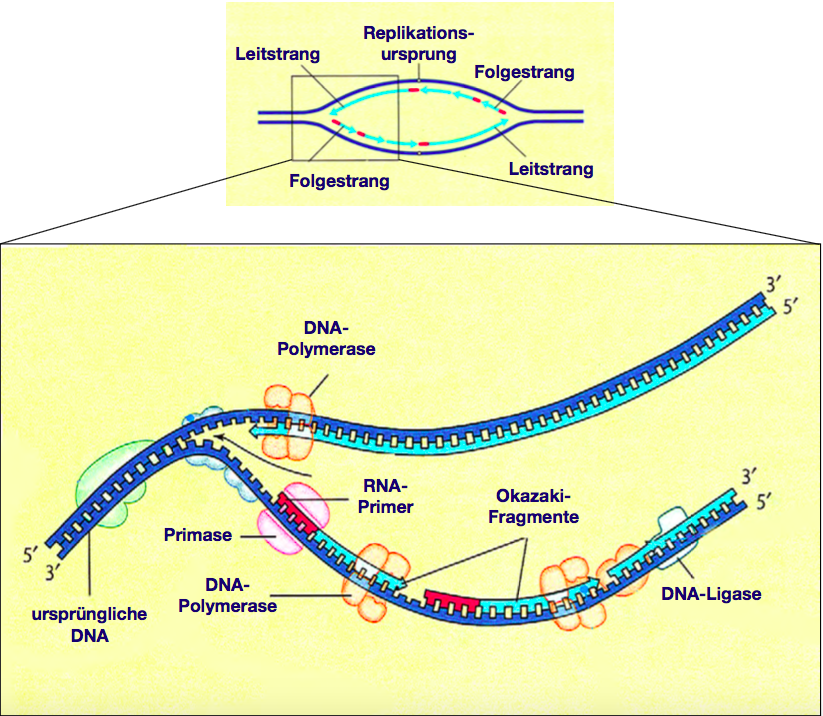
Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. Dna ligase connects the okazaki fragments by sealing the nick between fragments. This happens because dna polymerases can only read the dna template from the 5' to the 3' end and add free. The gaps between okazaki fragments and new dna fragments are joined by ligase. It has important role in the process of dna replication and dna repair. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. This type of replication is called discontinuous. Dna replication is the process in which new copy of dna is produced from parent dna. During dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the structural integrity of the genome.
Since the direction of movement of replication fork is opposite to direction dna replikation ligase. Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the structural integrity of the genome.
Dna Replikation Ligase Funktion: Removes rna primer and adds deoxyribonucleotides in its place.
comment 0 Post a Comment
more_vert